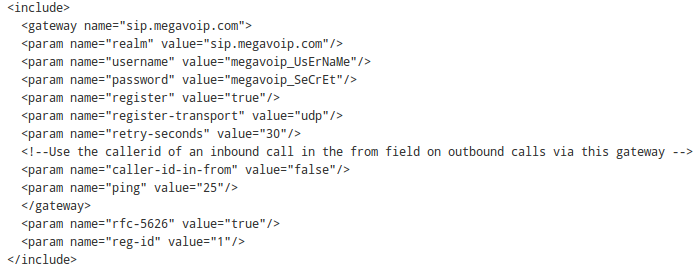
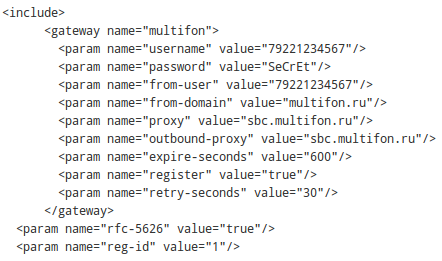
1. Edit postgresql.conf line listen_addresses = '10.14.1.21' to your appropriate value.
2. Add to pg_hba.conf a line, which will allow connection to the database from certain IP address/subnet: host johnsdb john 10.14.1.201/32 md5
3. service postgresql reload
4. As root, ‘su - postgres‘ , then ‘psql‘ , then:
4.1. postgres=# CREATE USER john WITH ENCRYPTED PASSWORD 'johnstailislong' ;
4.2. postgres=# CREATE DATABASE johnsdb WITH OWNER john ;
( If the database owner is wrong, change it: postgres=# ALTER DATABASE johnsdb OWNER TO john ; )
5. Then connect from outside to the already created database and create a table inside it:
psql -d johnsdb -U john -h 10.14.1.21
johnsdb=> CREATE TABLE johnstable (type varchar(6),name varchar(128),secret varchar(128),context varchar(128),host varchar(128)) WITH (OIDS=FALSE);
Hints:
Change DB’s owner (as postgresql user):
ALTER DATABASE johnsdb OWNER TO john ;
Change table’s owner (as postgresql user):
ALTER TABLE johnstable OWNER TO john ;
Table permissions: (as postgresql user):
GRANT ALL ON TABLE johnstable TO john ;
Change default values in a column:
ALTER TABLE tablename ALTER COLUMN columnname SET DEFAULT 'green,red' ;
Rename a column:
ALTER TABLE tablename RENAME COLUMN oldcolname TO newcolname;
Change column type:
ALTER TABLE tablename ALTER COLUMN columnname TYPE varchar(30);
Get last N rows:
SELECT * FROM mytable ORDER BY record_date DESC LIMIT 5;
Get first N rows:
SELECT * FROM mytable ORDER BY record_date ASC LIMIT 5;
Select between X and Y values:
SELECT name,callerid FROM sip_conf WHERE name BETWEEN '1301' and '1310' ORDER BY name;
Show databases:
astertest=> \list
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+-----------+----------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------
astertest | astertest | UTF8 | ru_RU.UTF-8 | ru_RU.UTF-8 |
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | ru_RU.UTF-8 | ru_RU.UTF-8 |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | ru_RU.UTF-8 | ru_RU.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | ru_RU.UTF-8 | ru_RU.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
(4 rows)
Show tables in the current database:
astertest=> \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------------------------+----------+-----------
public | sip_conf_office | table | astertest
public | sip_conf_office_id_seq | sequence | astertest
(2 rows)
Show table structure:
astertest=> \d sip_conf_office
Table "public.sip_conf_office"
Column | Type | Modifiers
----------------+------------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------
id | integer | not null default nextval('sip_conf_office_id_seq'::regclass)
name | character varying(80) | not null default ''::character varying
accountcode | character varying(20) |
amaflags | character varying(7) |
callgroup | character varying(10) |
callerid | character varying(80) |
canreinvite | character varying(3) | default 'no'::character varying
context | character varying(80) |
defaultip | character varying(15) |
dtmfmode | character varying(7) |
fromuser | character varying(80) |
fromdomain | character varying(80) |
host | character varying(31) | not null default ''::character varying
insecure | character varying(4) |
language | character varying(2) |
mailbox | character varying(50) |
md5secret | character varying(80) |
nat | character varying(5) | not null default 'no'::character varying
...
To insert many lines in SQL-syntax from txt file:
psql -U asterisk -h localhost -d asterisk -f /root/peers.txt
… assuming that peers.txt looks like:
INSERT INTO sip_conf_new (name,callerid,defaultuser,context,port) VALUES ('0001','Operator 0001 <0001>','0001','operators','5060');
INSERT INTO sip_conf_new (name,callerid,defaultuser,context,port) VALUES ('0001d','Operator 0001 <0001>','0001d','operators','5061');
INSERT INTO sip_conf_new (name,callerid,defaultuser,context,port) VALUES ('0002','Operator 0002 <0002>','0002','operators','5060');
INSERT INTO sip_conf_new (name,callerid,defaultuser,context,port) VALUES ('0002d','Operator 0002 <0002>','0002d','operators','5061');
...
INSERT INTO sip_conf_new (name,callerid,defaultuser,context,port) VALUES ('9999','Operator 9999 <9999>','9999','operators','5060');
INSERT INTO sip_conf_new (name,callerid,defaultuser,context,port) VALUES ('9999d','Operator 9999 <9999>','9999d','operators','5061');