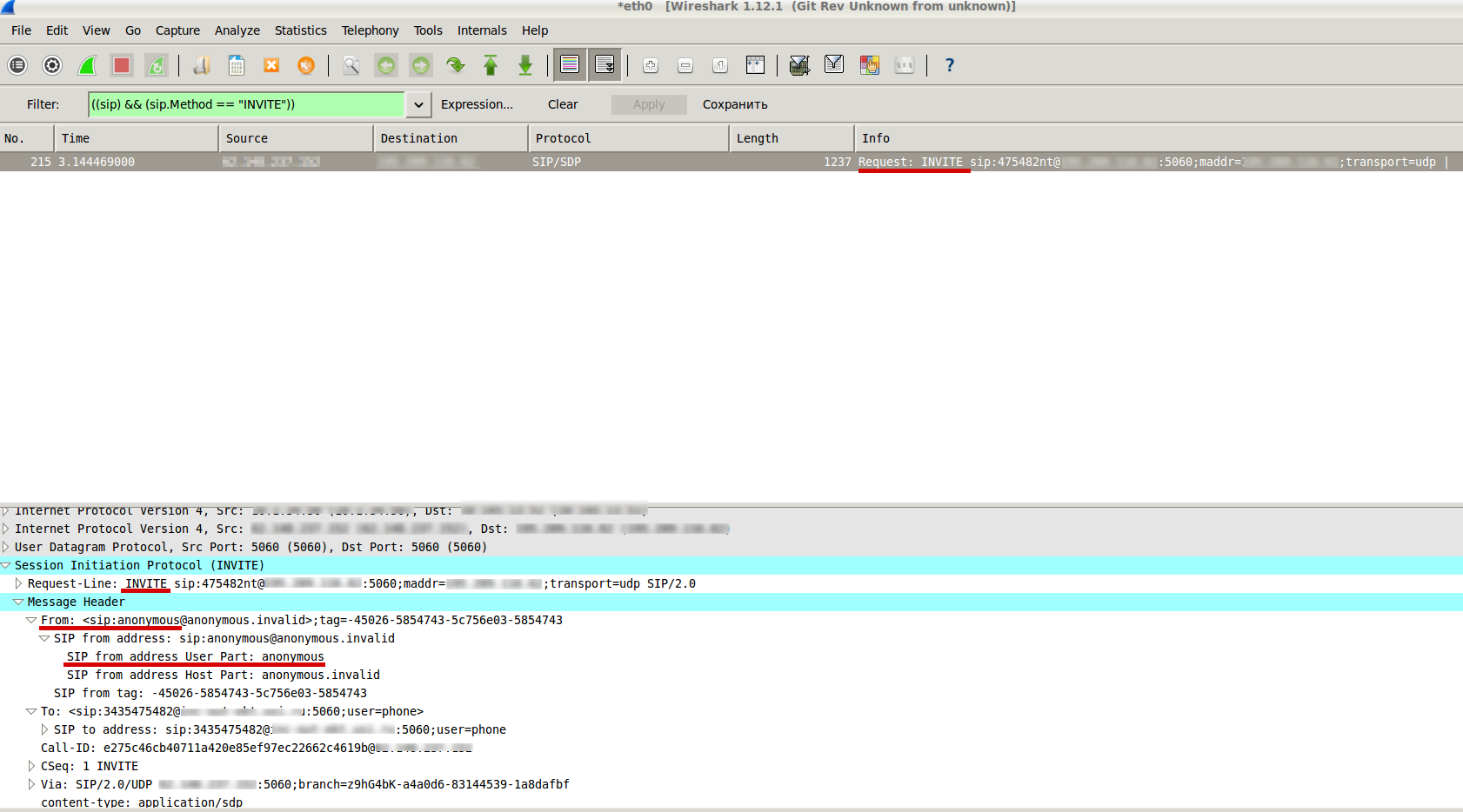
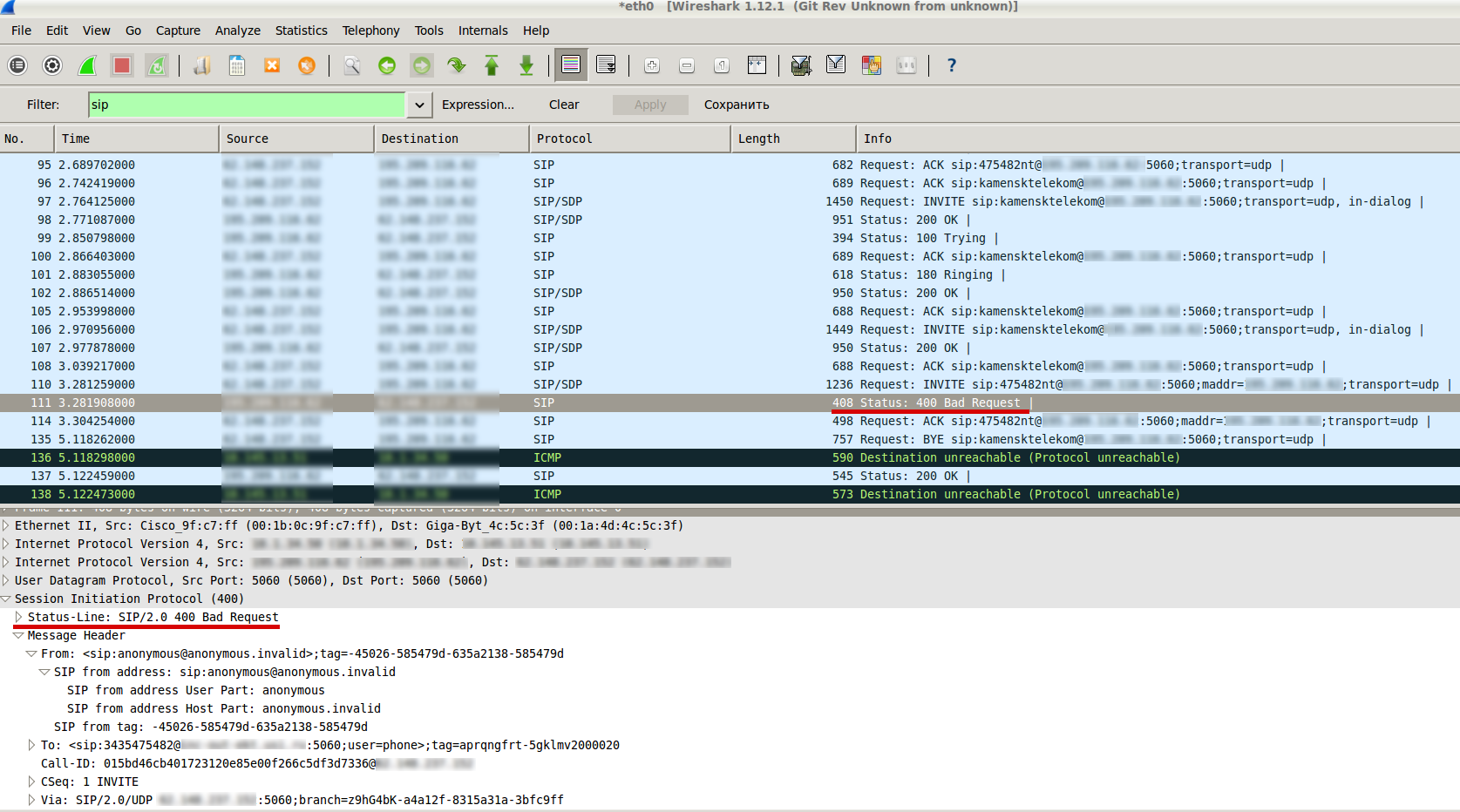
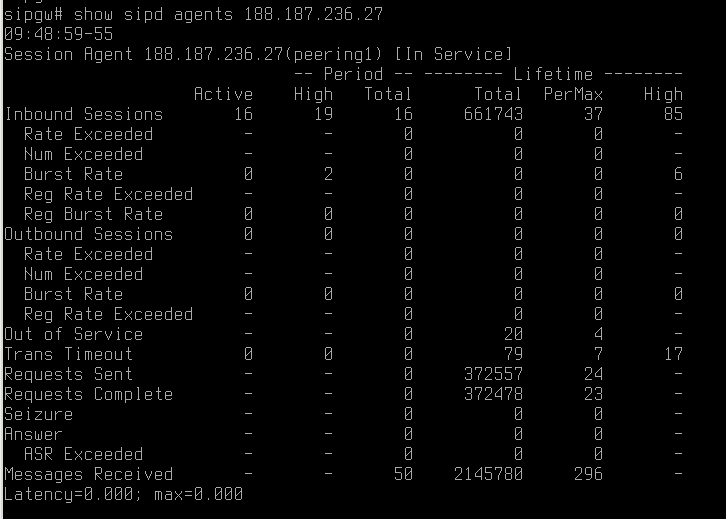
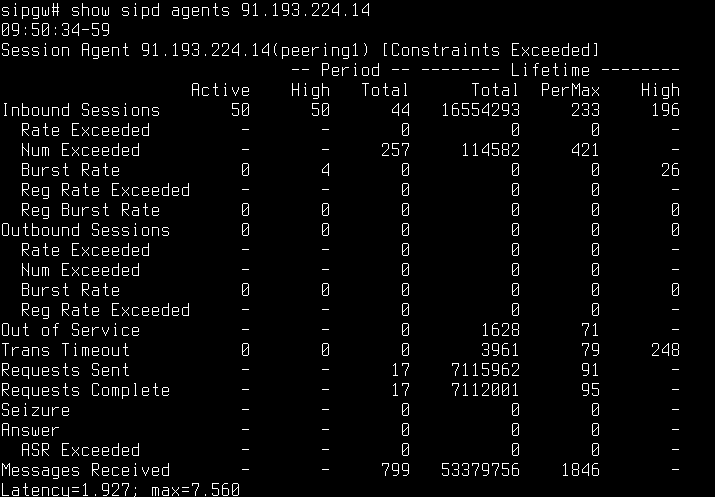
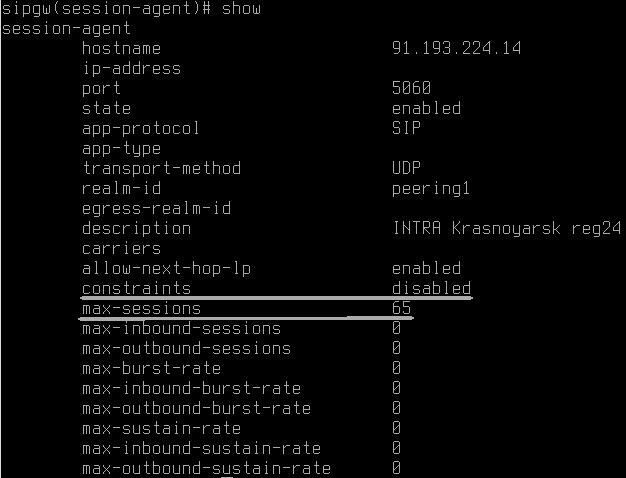
Depending on GSM operator the values in SIP headers may vary. In my case if a subscriber activated the ability to hide cell number, the ‘uri-user’ parameter in SIP-header ‘From’ contains not cell number but ‘anonymous’. I had a task to reject such calls.
There already were 2 header-rules – one doing storing of ‘To’ headers’ values with VoIP provider’s DIDs inside , and the second – manipulating the ‘From’ headers, according to the stored values.
If I added the 3rd header-rule (last in the list) trying to reject anonymous calls, it haven’t worked, so it was necessary to keep it on the top of header-rules. (the ‘move’ command doesn’t work for me, though I’ve read in one Oracle/AcmePacket HMR guide that it’s possible, maybe my firmware does not support it)
Here’s the rule itself:
header-rule name rejectAnonymous header-name From action manipulate comparison-type case-insensitive msg-type request methods INVITE match-value new-value element-rule name rejAnonymous parameter-name From type uri-user action reject match-val-type any comparison-type case-insensitive match-value Anonymous new-value
Have a look at these nice screenshots demonstrating the initial INVITE from anonymous:
… and rejecting this call by AcmePacket 4250 with ‘400 Bad Request’ response: