Mass upgrade of all packages is strongly discouraged and there is no any opkg command for upgrading all installed packages. But if you need it, run:
opkg list-upgradable | cut -f 1 -d ' ' | xargs -r opkg upgradeMass upgrade of all packages is strongly discouraged and there is no any opkg command for upgrading all installed packages. But if you need it, run:
opkg list-upgradable | cut -f 1 -d ' ' | xargs -r opkg upgradeTried in Lubuntu 24.04.3 LTS, should work in all *buntu.
To disable:
sudo dpkg-divert --package im-config --rename /usr/bin/ibus-daemon
… and then reboot. To enable back:
sudo dpkg-divert --package im-config --rename --remove /usr/bin/ibus-daemonThis is almost the same as I’ve already posted.
The difference is that now we will kill dialogs not based by the remote side IP address, but based on datestart. There was some short-term connectivity interruption which caused a sudden increase in dialogs count. It’s normal for such a situation and they will end by the configured lifetime (‘default_timeout‘ parameter), e.g. 1 hour.
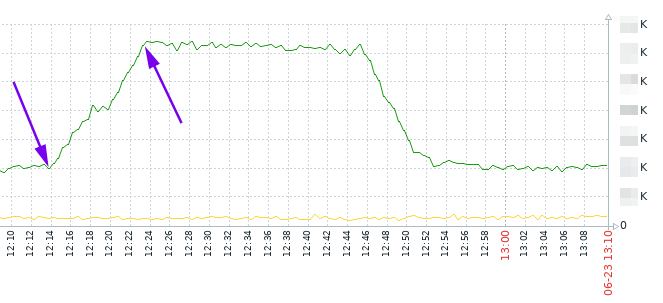
But what if we don’t want to wait and if we want to kill them manually?
The idea is to pick dialogs which were created during time range, assuming that you know an average call duration, and it’s obvious that if such calls are still shown by ‘opensips-cli -x mi dlg_list’ , it means that it is not valid alive call and you can kill it.
As it’s seen on the graph, the increasing was between 12:14 and 12:23. Let’s say it’s 12:30 now, and an average call duration is 30 … 60 seconds. So, we can kill dialogs which were created between 12:14 and 12:23 and which are still visible with ‘opensips-cli -x mi dlg_list’.
opensips-cli -x mi dlg_list > 2025-06-23_dlg_list.txtgrep datestart -B5 2025-06-23_dlg_list.txt | grep -B5 "2025-06-23 12:14:" | grep ID | awk '{ print $2}' | sed 's/"//g' | sed 's/,//g' > dlgs_12-14.txt
grep datestart -B5 2025-06-23_dlg_list.txt | grep -B5 "2025-06-23 12:15:" | grep ID | awk '{ print $2}' | sed 's/"//g' | sed 's/,//g' > dlgs_12-15.txt… and so on, up to 12:23. After that you’ll have several txt files with dialog IDs. Not it’s time to kill them:
for i in `echo $(cat dlgs_12-14.txt)` ; do opensips-cli -x mi dlg_end_dlg $i ; done… and the same for each file.
So, as a summary commands set we may use this one (just setting date/time you need):
# remove old files, if they are
rm -f dlgs_all.txt dlgs_to_kill.txt
# get all dialogs list
opensips-cli -x mi dlg_list > dlgs_all.txt
# just show the oldest dialog and the newest dialog
grep datestart dlgs_all.txt | sort | head -n1 ; echo ; grep datestart dlgs_all.txt | sort | tail -n1
# kill all dialogs started at e.g. 2025-08-21 15:0x
grep datestart -B5 dlgs_all.txt | grep -B5 "2025-08-21 15:0" | grep ID | awk '{ print $2}' | sed 's/"//g' | sed 's/,//g' > dlgs_to_kill.txt && for i in `echo $(cat dlgs_to_kill.txt)` ; do opensips-cli -x mi dlg_end_dlg $i ; done
Imagine the situation: you have an SQL table with some string in some column. There is a plenty of such rows, and you want to replace this string in each row with some other string, something like in Bash – sed ‘s/green apple/blue apple/g’.
The original table looks like this.
Select:
SELECT "prefix", "description", "ruleid"
FROM "dr_rules"
WHERE "description" LIKE '%from ACME%'
ORDER BY "ruleid"
DESC LIMIT 5;Result:
prefix description
73843444445 Novokuznetsk from ACME
73843208507 Novokuznetsk from ACME
73843400000 Maxim Novokuznetsk from ACME
73843208505 Office Poehali Novokuznetsk from ACME
73843208508 Office Maxim Novokuznetsk from ACME
We want to change “from ACME” to “moved from ACME”.
First, let’s test our SQL statement with SELECT, no changes will be made:
SELECT REPLACE(description,'from ACME','moved from ACME')
FROM dr_rules
WHERE description LIKE('%from ACME%')
AND description NOT LIKE('%moved from ACME');Now do an SQL UPDATE in a sed-like style:
UPDATE dr_rules
SET description=REPLACE(description,'from ACME','moved from ACME')
WHERE description LIKE('%from ACME%')
AND description NOT LIKE('%moved from ACME');The result after an UPDATE:
prefix description
73843444445 Novokuznetsk moved from ACME
73843208507 Novokuznetsk moved from ACME
73843400000 Maxim Novokuznetsk moved from ACME
73843208505 Office Poehali Novokuznetsk moved from ACME
73843208508 Office Maxim Novokuznetsk moved from ACME
So, to test the statement, do:
SELECT REPLACE(columnname,'old string','new string')
FROM tablename
WHERE columnname LIKE('%old string%')
AND columnname NOT LIKE('%new string');To replace, do:
UPDATE tablename
SET columnname=REPLACE(columnname,'old string','new string')
WHERE columnname LIKE('%old string%')
AND columnname NOT LIKE('%new string');If you need case-insensitive, use ILIKE instead of LIKE.
Let’s skip playing an annoying greeting for the caller, if he already called us withing the last 10 minutes.
Create a macro:
macro greetBlock( ext )
{
if(${DB_EXISTS(greetblock/${CALLERID(num)})}) {
// get the last call's timestamp.
Set(LASTCALL=${DB(greetblock/${CALLERID(num)})});
} else {
Set(LASTCALL=0);
}
Set(NOW=${EPOCH});
Set(DIFF=${MATH(${NOW} - ${LASTCALL},int)});
if ("${LASTCALL}" != "" & ${DIFF} < 600) {
// a person called less than 10 minutes ago - skip greeting.
NoOp(skip greeting to ${CALLERID(num)} for ${ext});
Set(GREETING=0);
} else {
Set(DB(greetblock/${CALLERID(num)})=${NOW});
Set(GREETING=1);
}
return;
};And use this macro in your dialplan:
73333123456 =>
{
NoOp(${STRFTIME(,,%F %R)} . ${CALLERID(num)} dials SALES office . callid start: ${SIP_HEADER(Call-ID)});
&greetBlock(${EXTEN});
if ("${GREETING}" = "1") {
goto greeton;
} else {
goto greetoff;
}
greeton:
Playback(${SOUNDS}/welcome);
greetoff:
Queue(...);
...
}Use case 1:
convert the username consisting of letters in incoming INVITE from your VoIP provider to digits
(e.g. INVITE: rt_user1@192.168.1.203 -> INVITE: 13511654321@192.168.1.203, where country-city-subscriber is 1-3511-654321):
Add to your dialplan table:
INSERT INTO dialplan VALUES \
(1002,0,0,'rt_user1',1,'','13511654321',NULL,0,'modifying letters to digits in provider''s ruri');So, the SQL record is as follows:
sqlite> select * from dialplan where dpid=1002;
id = 2
dpid = 1002
pr = 0
match_op = 0 # Matching operator for rule (0-equal, 1-regexp).
match_exp = rt_user1
match_flags = 1
subst_exp =
repl_exp = 13511654321
timerec =
disabled = 0
attrs = modifying letters to digits in provider's ruriOpenSnitch – a Linux firewall for applications – interactive outbound connections filtering.
https://www.linux-magazine.com/index.php/Issues/2022/259/OpenSnitch
https://github.com/evilsocket/opensnitch
Nice oneliners which may be useful to show some console output via HTTP.
An example of showing the iptables FORWARD chain:
while true ; do echo -e "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n\n $(sudo iptables -L FORWARD -vn --line-numbers)" | nc -l -p 8080 -q 1; doneThen go to http://ip.add.re.ss:8080 and you will see the output as a web page. In case of adding new rules renew the webpage and you will see the newly added rules.
To report file system disk space usage:
while true ; do echo -e "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n\n $(df -h)" | nc -l -p 8080 -q 1; doneMore info: https://www.linux-magazine.com/Issues/2021/250/Bash-Web-Server/(offset)/3/(tagID)/92#